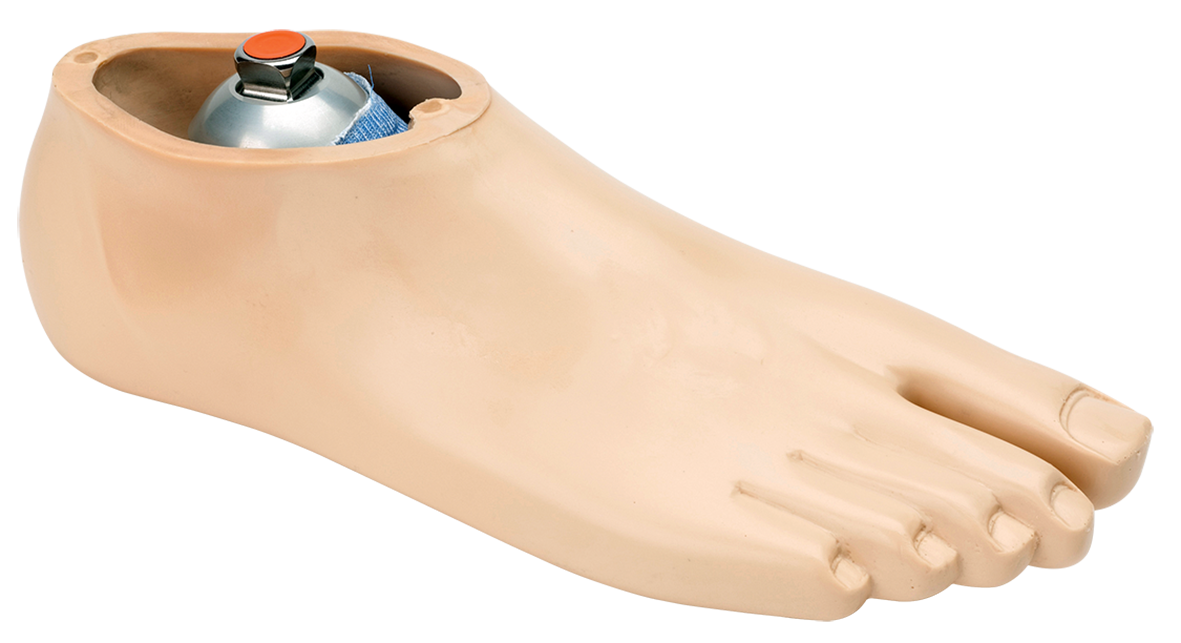
Navigator
The stability and comfort provided by the navigator multi-axial prosthetic foot with flexible keel ensures that users with an activity level of 1-3 are safer on uneven ground. The ankle centre is positioned anatomically to promote a natural gait from heel strike to toe off.
- Activity level 1
- Activity level 2
- Suitable for outdoor use
- Activity level 3
Navigator Clinical Evidence Reference
Clinical Outcomes using Navigator
-
Mobility
- Shorter keel allows for more consistent rollover radius of curvature, regardless of changing footwear1
- The most energy efficient radius of curvature for a rollover shape has been identified as 30% of the walker’s leg length. For a person of a typical adult height between 1.5m and 1.8m, this equates to approximately 245-290mm. Navigator has a rollover shape of ~250mm1.
Clinical Outcomes using Multiflex-style ankles
-
Safety
- Low stiffness at weight acceptance leads to early foot-flat and greater stability for lower mobility patients15
- No loss of stability during standing with Multiflex than fixed ankle/foot16
- Easier to walk on uneven ground with Multiflex than fixed ankle/foot16,17
- Easier to walk up a slope with Multiflex than fixed ankle/foot16
-
Mobility
- Little to no difference in gait mechanics compared to flexible, “energy storing” prosthetic feet18
- Increased prosthetic ankle range-of-motion with Multiflex compared to fixed ankle/foot16,17,19-21
- Increased prosthetic ankle power with Multiflex compared to fixed ankle/foot17
- Prosthetic rollover shape closer to natural biomechanics than fixed ankle/foot19
- Users can walk longer distances and report “smoother” gait with Multiflex compared to fixed ankle/foot17
- Benefits in mobility for bilateral users17,19-21
-
Residual Limb Health
- Equivalent socket comfort to higher technology, energy-storing feet22
-
Loading symmetry
- Improved stance phase timing symmetry with Multiflex compared to fixed ankle/foot21
- Reduced sound limb loading with Multiflex compared to fixed ankle/foot21
-
User satisfaction
- Majority of users rate Multiflex as either “good” or “acceptable”23 and prefer Multiflex to fixed ankle/foot17
References
-
Full Reference Listing
-
Curtze C, Hof AL, van Keeken HG, et al.
Comparative roll-over analysis of prosthetic feet. J Biomech 2009; 42: 1746–1753.
-
Moore R.
Patient Evaluation of a Novel Prosthetic Foot with Hydraulic Ankle Aimed at Persons with Amputation with Lower Activity Levels. JPO J Prosthet Orthot 2017; 29: 44–47.
-
Moore R.
Effect on stance phase timing asymmetry in individuals with amputation using hydraulic ankle units. JPO J Prosthet Orthot 2016; 28: 44–48.
-
Buckley JG, De Asha AR, Johnson L, et al.
Understanding adaptive gait in lower-limb amputees: insights from multivariate analyses. J Neuroengineering Rehabil 2013; 10: 98.
-
Sedki I, Moore R.
Patient evaluation of the Echelon foot using the Seattle Prosthesis Evaluation Questionnaire. Prosthet Orthot Int 2013; 37: 250–254.
-
Rogers JP, Strike SC, Wallace ES.
The effect of prosthetic torsional stiffness on the golf swing kinematics of a left and a right‐sided trans‐tibial amputee. Prosthet Orthot Int 2004; 28: 121–131.
-
Kobayashi T, Orendurff MS, Boone DA.
Dynamic alignment of transtibial prostheses through visualization of socket reaction moments. Prosthet Orthot Int 2015; 39: 512–516.
-
Wright DA, Marks L, Payne RC.
A comparative study of the physiological costs of walking in ten bilateral amputees. Prosthet Orthot Int 2008; 32: 57–67.
-
Vanicek N, Strike SC, Polman R.
Kinematic differences exist between transtibial amputee fallers and non-fallers during downwards step transitioning - Natalie Vanicek, Siobhán C Strike, Remco Polman, 2015. ProsthetOrthot Int 2015; 39: 322–332.
-
Barnett CT, Vanicek N, Polman R, et al.
Kinematic gait adaptations in unilateral transtibial amputees during rehabilitation: Prosthetics and Orthotics International: Vol 33, No 2. Prosthet Orthot Int 2009; 33: 135–147.
-
Emmelot CH, Spauwen PHM, Hol W, et al.
Case study: Trans‐tibial amputation for reflex sympathetic dystrophy: Postoperative management. Prosthet Orthot Int 2000; 24: 79–82.
-
Boonstra AM, Fidler V, Eisma WH.
Walking speed of normal subjects and amputees: Aspects of validity of gait analysis. Prosthet Orthot Int 1993; 17: 78–82.
-
Datta DD, Harris I, Heller B, et al.
Gait, cost and time implications for changing from PTB to ICEX® sockets. Prosthet Orthot Int 2004; 28: 115–120.
-
Castro M de, Soares D, Mendes E, et al.
Center of Pressure Analysis During Gait of Elderly Adult Transfemoral Amputees. J Prosthet Orthot 2013; 25: 68–75.
-
Major MJ, Scham J, Orendurff M.
The effects of common footwear on stance-phase mechanical properties of the prosthetic foot-shoe system. Prosthet Orthot Int 2018; 42: 198–207.
-
McNealy LL, Gard SA.
Effect of prosthetic ankle units on the gait of persons with bilateral trans-femoral amputations. Prosthet Orthot Int 2008; 32: 111–126.
-
Su P-F, Gard SA, Lipschutz RD, et al.
Gait characteristics of persons with bilateral transtibial amputations. J Rehabil Res Dev 2007; 44: 491–502.
-
Boonstra A, Fidler V, Spits G, et al.
Comparison of gait using a Multiflex foot versus a Quantum foot in knee disarticulation amputees. Prosthet Orthot Int 1993; 17: 90–94.
-
Gard SA, Su P-F, Lipschutz RD, et al.
The Effect of Prosthetic Ankle Units on Roll-Over Shape Characteristics During Walking in Persons with Bilateral Transtibial Amputations. J Rehabil Res Dev 2011; 48: 1037.
-
Major MJ, Stine RL, Gard SA.
The effects of walking speed and prosthetic ankle adapters on upper extremity dynamics and stability-related parameters in bilateral transtibial amputee gait. Gait Posture 2013; 38:858–863.
-
Van der Linden ML, Solomonidis SE, Spence WD, et al.
A methodology for studying the effects of various types of prosthetic feet on the biomechanics of trans-femoral amputee gait. J Biomech 1999; 32: 877–889.
-
Graham LE, Datta D, Heller B, et al.
A comparative study of conventional and energy-storing prosthetic feet in high-functioning transfemoral amputees. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2007; 88: 801–806.
-
Mizuno N, Aoyama T, Nakajima A, et al.
Functional evaluation by gait analysis of various ankle-foot assemblies used by below-knee amputees. Prosthet Orthot Int 1992; 16: 174–182
-